The Comparison of Self-assessment of Confidence and Venipuncture Skill among the Third-Year Nursing Students Utilizing a Venipuncture Training Model: Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Udon Thani
Keywords:
Venipuncture training model, confidence, venipuncture skillAbstract
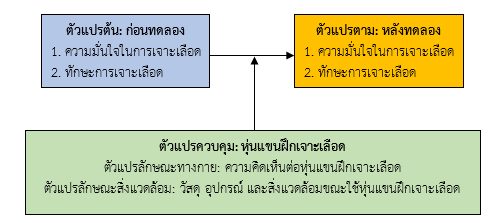
Venipuncture, a crucial nursing skill, requires precise practice for nursing students. However, limited opportunities hinder their training. To address this, Boromarajonani College of Nursing, Udon Thani, has developed a Venipuncture Training Model (VTM). The objective of this research was to compare self-assessment of confidence and venipuncture skill among the third-year nursing students utilizing a VTM. The study involved 71 nursing students. Data collection tools included a questionnaire of comparing self-assessment of confidence and venipuncture skill before and after using the VTM. The IOC tool had a validity coefficient of 0.72, and the Cronbach's alpha coefficient was 0.88. The data was analyzed using descriptive statistics and paired sample t-tests.
The research findings showed positive overall perceptions towards the VTM at good level, including production (M = 4.07, SD = 0.84), utilization (M = 4.14, SD = 0.80) and maintenance (M = 4.19, SD = 0.81). The confidence and venipuncture skill after self-training with the VTM were significantly higher than before training (r = 0.09, p-value < 0.001; r = 0.15, p-value < 0.001).
The results of this study can be used as the initial input for venipuncture training, fluid administration, and relevant innovations in the future.
References
ธารินี นนทพุทธ, และ ปฐมามาศ โชติบัณ. (2564). การพัฒนานวัตกรรมหุ่นฝึกการให้สารน้ำบริเวณแขน. วารสารเครือข่ายวิทยาลัยพยาบาลและการสาธารณสุขภาคใต้, 8(3), 49-60.
ตรีนุช พุ่มมณี, จุฑามาศ สุวรรณวัฒน์, กรวิกา บวชชุม, อรวรรณ หนูแก้ว, พิเชษฐ์ สุวรรณจินดา, ภัทราภรณ์ วรสิรินารา. (2566). ผลของสื่อวีดิทัศน์การสอนเรื่องการตรวจสภาพจิตร่วมกับการเรียนรู้โดยใช้กรณีศึกษาต่อความรู้ ความมั่นใจและความพึงพอใจของนักศึกษาพยาบาลหลักสูตรพยาบาลศาสตรบัณฑิตในรายวิชาปฏิบัติการพยาบาลสุขภาพจิตและจิตเวช. วารสารวิจัยทางการพยาบาล การผดุงครรภ์และวิทยาศาสตร์สุขภาพ, 43(1), 67-79.
นพวรรณ บุญบำรุง และ ศุทธิจิต ภูมิวัฒนะ. (2557). ประสิทธิผลของโปรแกรมการฝึกทักษะการดูดเสมหะทางท่อทางเดินหายใจเทียมโดยใช้สถานการณ์จำลองต่อความรู้ ทักษะ และความมั่นใจในนักศึกษาพยาบาลชั้นปีที่ 3 วิทยาลัยพยาบาลสภากาชาดไทย. วารสารสภากาชาดไทย, 7(1), 38-47.
เบญญพร บรรณสาร. (2560). การประดิษฐ์หุ่นแขนผู้ใหญ่แบบพกพา เพื่อฝึกการเจาะเลือด และการเปิดเส้นเลือดให้สารน้ำทางหลอดเลือดดำสำหรับนักศึกษาพยาบาล. วารสารการพยาบาล, 32(8): 38-49.
สุภลักษณ์ เชยชม และ ดลรัตน์ รุจิวัฒนากร. (2558). การใช้นวัตกรรมหุ่นแขนในการฝึกหัตถการให้สารน้ำทางหลอดเลือดดำของนักศึกษาพยาบาล. รามาธิบดีพยาบาลสาร, 21(3), 395-407.
อภิรดี นันท์ศุภวัฒน์, นงค์คราญ วิเศษกุล, ปิยวรรณ สวัสดิ์สิงห์, ศันสนีย์ เอื้อพันธ์วิริยะกุล, และ สุสัณหา ยิ้มแย้ม. (2565). การพัฒนาหุ่นจำลองแขนให้สารละลายทางหลอดเลือดดำ. วารสารพยาบาลสารมหาวิทยาลัย เชียงใหม่, 49(3), 311-323.
อะเคื้อ อุณหเลขกะ และ สุชาดา เหลืองอาภาพงศ์. (2556). การป้องกันอุบัติเหตุจากเข็มและของมีคมของโรงพยาบาลในประเทศไทย. พยาบาลสาร. 40(พิเศษ): 130-142.
Buchne, A. (2010). G*Power: Users Guide-Analysis by design. Web Page of Heinrich-Heine-Universitat - Institut fur experimentelle Psychologie
Buowari, O. Y. (2013). Complications of venipuncture. Advances in Bioscience and Biotechnology. 4(1A), 8-126.
Colledge H. (2015). What are the most common intravenous complication?. Retrieved 8 April 2024 from http://www.wisegeek.org/whatare-the-most-common-intravenouscomplications.htm
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Buchner, A. & Lang, A.G. (2009). Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behavior Research Methods. 41, 1149-1160.
Jarintanan, F., Chanprasert, K., Kongwan, W., Ratanawiboolsook, N., Pawinwongcha, J., & Liemmanee, W. (2016). Rubber arm with fluid system for venipuncture training, new model in clinical skills tutors. Science and technology RMUTT Journal, 6(1), 212-220.
Garus-Pakowska, A. & Górajski, M. (2019). Behaviors and attitudes of polish health care workers with respect to the hazards from blood-borne pathogens: A questionnaire-based study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(5), 891-904.
Honda, M., Chompikul, J., Rattanapan, C., Wood G. & Klungboonkrong S. (2011). Sharps injuries among nurses in a Thai regional hospital: prevalence and risk factors. International Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine, 2(4), 215-223.
Kelley, D. & Kelley, T. (2013). Creative Confidence: Unleashing he Creative Potential within us all. New York: Crown.
Motaarefi, H., Mahmoudi, H., Mohammadi, E. & Hasanpour-Dehkordi, A. (2016). Factors associated with needle stick injuries in health care occupations: A systematic review. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research, 10(8), IE01–IE04.
Meunya, S., Nualthong, W., Thongtang, P. & Thepthongkum, D. (2014). Factors influencing nursing skills on perception of student nurses after their clinical practiced in principles and techniques in nursing practicum, Boromarajonani college of nursing, Uttaradit. Journal of Nursing and Health Sciences. 6(3), 200-211. (In Thai)
Saengpayab, Y., Kongsri, W., Chongsereecharoen, E., Pratummasoot, N., Akkarapattanapong, V. & Jarintanan, F. (2020). Venipuncture training assists using electrical sensors in a rubber arm system. Journal of Physics: Conference series, 3(1719), 1-7.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Praboromarajchanok Institute

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





