The Effect of IDEAL Model Neonatal Jaundice Discharge Planning Program On Caregiver's Knowledge and Skill
Abstract
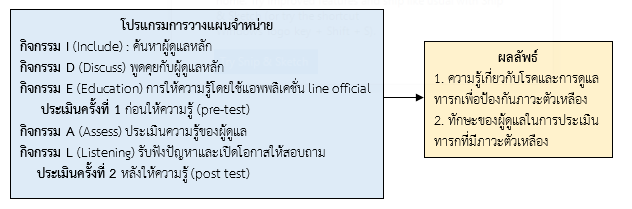
This quasi-experimental study (One group Pre-test Post-test) aimed to develop a discharge planning program for Neonatal Jaundice in infants to enhance caregivers' knowledge and skills using the IDEAL Discharge Planning Strategy, covering 3C-PDSA. The study applied the development process according to the clinical practice development framework of the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (NHMRC). Additionally, it aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of the discharge planning program in studying caregivers of jaundiced infants, totaling 30 participants. Research instruments included pre-test and post-test knowledge questionnaires, pre-test and post-test skills assessments, validated for content validity with a CVI value of 1. The development of the jaundiced infant discharge planning program according to the IDEAL framework included steps, methods, and content aligned with the 5-letter framework, namely, Include, Discuss, Educate, Assess, and Listen; I (Include): Identified primary caregivers, involving them in care and discharge planning, D (Discuss): Engaged in discussions with primary caregivers using the aforementioned 5 principles while visiting sick infants, E (Education): Educated caregivers about infant care upon returning home using the Line Official application named "Knowing Jaundice". A (Assess): Assessed caregivers' knowledge on each topic related to infant care to prevent jaundice. L (Listen): Listened to problems and gave caregivers the opportunity to ask further questions, organized through a Focus Group of mothers or caregivers of jaundiced infants receiving treatment, including discharge planning for continuous care at home. Post-test assessment (post-test) was conducted on the day of infant discharge. Data analysis was performed using Independent t-test and Paired t-test statistics.
The research findings revealed that the average scores for caregivers' knowledge of jaundiced infants in preventing readmissions after receiving the IDEAL discharge planning program were significantly higher than before (t = 9.953; p < .001). Similarly, the average scores for skills training of caregivers of jaundiced infants after receiving the IDEAL discharge planning program were significantly higher than before (t = 76.69; p < .001).
The IDEAL discharge planning program resulted in caregivers having accurate, appropriate, and confident knowledge and skills in caring for jaundiced infants, ensuring the safety of newborns from illnesses, and contributing to their quality of life.
References
กินรี ชัยสวรรค์ และธนพร แย้มสุดา. (2561). ปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับภาวะตัวเหลืองในทารกแรกเกิด. วารสารแพทย์นาวี, 45(2), 235-249.
พรรณวรดา สุวัน, ลุนนี ราชไชย, และณัฐวรรณ ชัยมีเขียว. (2562). ประสิทธิผลของการพัฒนารูปแบบการวางแผนจำหน่ายผู้ป่วยเบาหวานตามกรอบแนวคิด IDEAL โรงพยาบาลส่องดาว สกลนคร. วารสารพยาบาลศาสตร์และสุขภาพ, 42(2), 112-124.
วรรษมน ปาพรม. (2561). ผลของโปรแกรมสนับสนุนและแอปพลิเคชันให้ความรู้ต่อพฤติกรรมการดูแลของผู้ดูแลทารกแรกเกิดที่มีภาวะตัวเหลืองและได้รับการรักษาโดยการส่องไฟ. วารสารพยาบาลสงขลานครินทร์, 38(3), 167-178.
วราลี เดชพุทธวัจน์, และแสงแข ชำนาญวนกิจ. (2559). ประสิทธิผลของโคมส่องไฟฟลูออเรสเซนต์และกระโจมส่องไฟแอลอีดีในการรักษาภาวะตัวเหลืองในทารกแรกเกิด. เวชสารแพทย์ทหารบก, 69(2), 115-121.
ศิริมา มณีโรจน์. (2565). ผลของโปรแกรมการดูแลและวางแผนจำหน่ายโดยใช้ IDEAL Model ต่อความรู้ระดับน้ำตาลสะสม ความพร้อมในการจำหน่ายและอัตราการกลับมารักษาซ้ำในผู้ป่วยเบาหวานที่มีปัญหาซับซ้อน. มหาราชนครศรีธรรมราชเวชสาร, 6(1), 78-91.
สำนักนโยบายและยุทธศาสตร์กระทรวงสาธารณสุข. (2560). ยุทธศาสตร์ตัวชี้วัดและแนวทางการจัดเก็บข้อมูลกระทรวงสาธารณสุข ประจำปีงบประมาณ พ.ศ. 2560. กระทรวงสาธารณสุข.
Burke, R. E., Kripalani, S., Vasilevskis, E. E., & Schnipper, J. L. (2013). Moving beyond readmission penalties: Creating an ideal process to improve transitional care. Journal of Hospital Medicine, 8(2), 102-109. https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.1990
Chantanamongkon, K. (2011). Pediatric nursing. M&M Laser Print Limited Partnership.
Cohen, J. (1992). Quantitative methods in psychology: A power primer. Psychological Bulletin, 112(1), 155-159.
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Lang, A.-G., & Buchner, A. (2007). G Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behavior Research Methods, 39, 175-191.
Halasyamani, L., Halasyamani, S., Coleman, E., Schnipper, J., Van Walraven, C., Nagamine, et al. (2006). Transition of care for hospitalized elderly patients development of a discharge checklist for hospitalists. Journal of Hospital Medicine, 1(6), 354-360. Retrieved March 25, 2024 from https://doi.org/10.1002/jhm.129.
Israel, G. D. (1992). Sampling the evidence of extension program impact (PEOD-5). Program Evaluation and Organizational Development, IFAS, University of Florida.
Paprom, W. (2018). Effects of the supportive program and application towards care behavior of caregivers of newborns with neonatal hyperbilirubinemia undergoing phototherapy. Journal of Research in Nursing-Midwifery and Health Sciences, 38(3), 167-178. retrieved from https://he02.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/nur-psu/article/view/148290
Mosby's dictionary of medicine, nursing & health (3rd ed.). (2013). National Health and Medical Research Council.
National Health and Medical Research Council. (2013). A guideline to the development, implementation and evaluation of clinical practice guidelines. Retrieved March 25, 2024 from http://www.nhmrc.gov.au.
Nelson, J. M., & Rosenthal, L. (2015). How nurses can help reduce hospital readmissions. American Nurse Today, 10(5), 18-20.
Shepperd, S., McClaran, J., Phillips, C. O., Lannin, N. A., Clemson, L. M., McCluskey, A., et al. (2014). Discharge planning from hospital to home. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (1).
Shuster, J. J. Boca Raton, F. L. (1990). CRC Handbook of Sample Size Guidelines for Clinical Trials. CRC Press.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Praboromarajchanok Institute

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.





