Effective of clinical Nursing Practice Guideine(CNPG) intravenous fluid to prevent peripheral phlebitis inpatient Effective of clinical Nursing Practice Guidelines (CNPG) intravenous fluid to Prevent peripheral phlebitis inpatient Department at Sir Chiang Mai Hospital, Nong Khai Province.
Main Article Content
Abstract
This quasi-experimental research aimed to study the results of using nursing practice guidelines for intravenous fluid administration in the peripheral part. The population were 30 professional nurses working at Sri Chiang Mai Hospital and the sample group selected by purposive sampling using the inclusion criteria, totaling 14 people and study period was 8 weeks. The instruments used in the study were assessment form for using the intravenous fluid administration guidelines, the satisfaction questionnaire and Incidence of thrombophlebitis. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics with frequency, percentage, and mean, etc.
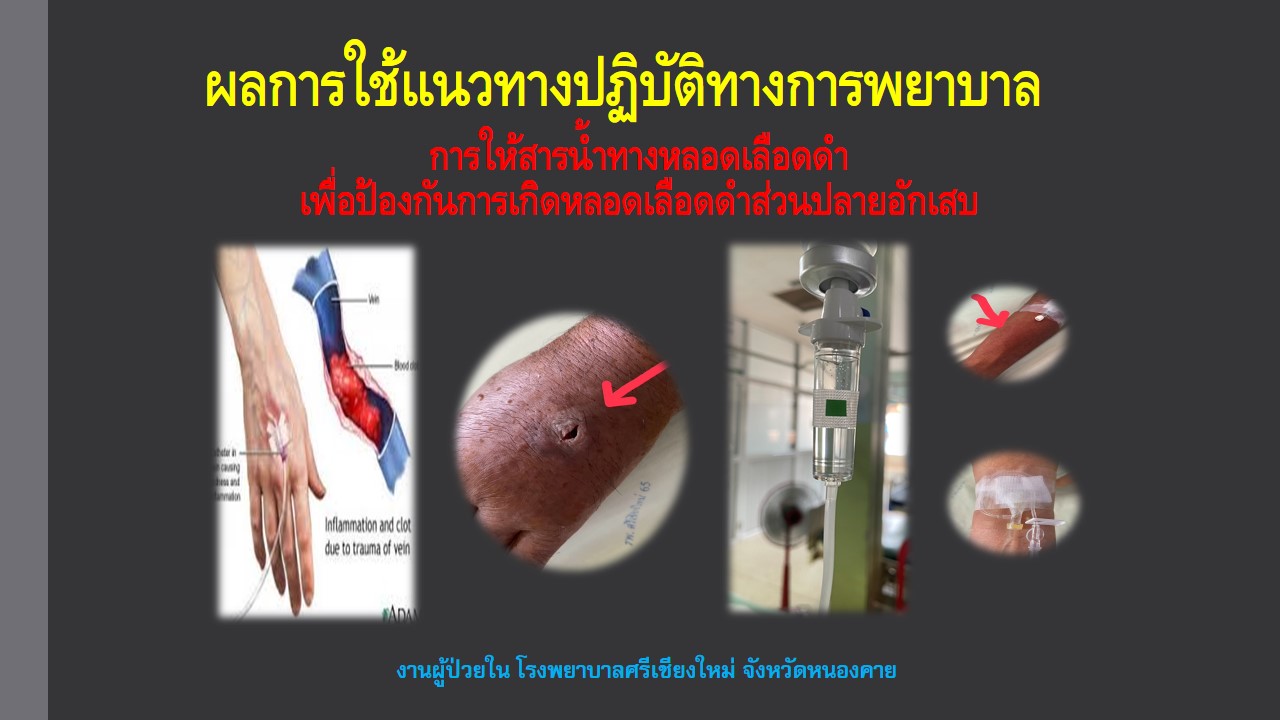
The results found that the majority of the sample group were female, accounting for 71.43 percent, single, accounting for 64.3 percent, aged between 20-25 years, the most at 42.85 percent, graduated with a bachelor's degree at 100 percent, most had 1-5 years of work experience, accounting for 57.14 percent, worked in an operating position at 64.3 percent, and denied chronic diseases, 13 people at 92.85 percent. After using the guidelines, it was found that the sample group had additional knowledge about intravenous fluid administration and was most satisfied at 98.04 percent. When comparing before and after using guidelines, it was found that the sample group was able to administer intravenous fluids correctly, increasing from 75.55 to 99.27 percent, and reducing the incidence of inflammation in the distal veins from 30 to 6 percent, respectively. It can be seen that the developed guidelines helped increase knowledge and skills in nursing activities, resulting in better results for patients in order.
Keywords : guidelines for nursing activities, Intravenous fluids, Peripheral phlebitis
Corresponding author : Monthian Kotchompoo Email : Monthiakcp@gmail.com
Article Details
References
O'Grady, N.P., Alerander, M., Dellinger, E. P., et al. (2002) Guidelines for the Prevention of Intravascular catheter Related infections Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. MMWR Recommendations and Reports, 51, 1-29.
ปาจรีย์ ศักดิ์วาลีสกุล, และอุษณีย์ ศิริวงศ์พรหม. ผลของแนวปฏิบัติการพยาบาลเพื่อป้องกันหลอดเลือดดำอักเสบจากการได้รับยานอร์อีพิเนฟริน. วารสารมหาวิทยาลัยคริสเตียน 2562 ;25(2):92-108.
Zheng GH, Yang L, Chen HY, Chu JF, Mei L. Aloe Vera for prevention and treatment of infusion phlebitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014; (6)
ฝ่ายการพยาบาล โรงพยาบาลศรีเชียงใหม่. (2566). ตัวชี้วัดคุณภาพการพยาบาล งานการพยาบาลผู้ป่วยในประจำปี พ.ศ. 2565-2567.
บุญใจ ศรีสถิตนรากูร. (2553). ระเบียบวิธีการวิจัยทางพยาบาลศาสตร์ (พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 5). กรุงเทพฯ: ยูแอนด์ไอ อินเตอร์ มีเดีย.
กันยา นภาพงษ์. (2560). การให้สารน้ำทางหลอดเลือดดำ. วิทยาลัยพยาบาลและสุขภาพ. กรุงเทพมหานคร: มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏ สวนสุนันทา.
ลักษณี มีนะนันท์. (2535). การให้สารน้ำทางหลอดเลือดดำ. ในสุปราณี วศินอมร (บรรณาธิการ), การพยาบาลพื้นฐาน แนวคิดและการปฏิบัติ (พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 6). กรุงเทพฯ: จุดทองการพิมพ์.
เพ็ญศรี นิลขำ.การพัฒนาแนวปฏิบัติทางคลินิกการพยาบาลผู้ป่วยที่ได้รับสารน้ำทางหลอดเลือดดำส่วนปลายตึกผู้ป่วยใน โรงพยาบาลแกดำ จังหวัดมหาสารคาม. วารสารวิชาการสำนักงานสาธารณสุขจังหวัดมหาสารคาม 2567; 8 (16): 227-241.
นภา อุทัยศรี. การพัฒนาแนวทางการปฏิบัติทางการพยาบาลเพื่อป้องกันการเกิดหลอดเลือดดำอักเสบ ของผู้ป่วยที่ได้ให้สารน้ำทางหลอดเลือดดำในงานการพยาบาลผู้ป่วยในโรงพยาบาลกู่แก้ว จังหวัดอุดรธานี. วารสารวิจัยสุขภาพโรงพยาบาลและชุมชน 2566; 1(3): 199-214.
Quick summary. (2020). CDC-HICPAC Guideline for the prevention of intravascular catheter related infections.
ไสว นรสาร. หลอดเลือดดำส่วนปลายอักเสบจากการให้สารน้ำ : ความเสี่ยงทางคลินิกที่ป้องกันได้. Rama Nurs J e 2006; 12 (2):167-176.
กาญจนา อุดมอัษฎาพร, และมยุรี พรมรินทร์. (2561). ประสิทธิผลของการใช้แนวทางปฏิบัติการป้องกันการอักเสบของหลอดเลือดดำและการรั่วซึมออกนอกหลอดเลือดดำ จากการใช้ยากระตุ้นการหดตัวของหลอดเลือด หอผู้ป่วยหนัก โรคหัวใจโรงพยาบาลเชียงรายประชานุเคราะห์.วารสารสาธารณสุขล้านนา, 14(1), 35-45.
Lisa A.G. Standard 53: Phlebitis. Journal of Infusion Nursing 2007; 30(5) : 265-266.